Teaching Kids Programming: Videos on Data Structures and Algorithms
The Birthday Candles Problem
If a person blows 1 candle at Age 1, 2 candles at Age 2, 3 candles at Age 3, then what is the year of the birthday if he/she has blown total 231 candles.
This can be solved using three algorithms/approaches.
The Bruteforce Algorithm
We can try brute forcing (perform a linear search) the year and compute the sum, until it reaches T (total) or exceed it.
def f(T):
year = 0
total = 0
while total < T:
year += 1
total += year
return year if total == T else -1
To understand the number of iterations, notice that the total is essentially the sum of the first n natural numbers, where n is the number of years. This sum is known to be  . The loop stops when this sum is greater than or equal to T. So, we’re looking for the smallest n such that:
. The loop stops when this sum is greater than or equal to T. So, we’re looking for the smallest n such that:

Solving this quadratic inequality gives us the smallest n that satisfies the condition. Since this is essentially forming a series, the number of iterations is proportional to the square root of T because you’re solving for n in a quadratic equation. This means the time complexity of the loop is O(√T).
The Binary Search Algorithm
We can binary search the range [1, T].
def f(T):
L = 1
R = T
while L <= R:
M = L + R >> 1
s = (M + 1) * M >> 1
if s == T:
return M
if s < T:
L = M + 1
else:
R = M - 1
return -1
The key to understanding the time complexity lies in the while loop and how quickly the range between L and R is reduced.
- Each iteration of the while loop approximately halves the search range.
- The initial range of values is from 1 to T.
- The number of times you can halve T until you get down to 1 (the smallest possible range) is

So, the while loop, which dominates the time complexity, runs in O(log T) time. Thus, the overall time complexity of the function is O(log T).
The Quadratic Equation Solver
Given the Year n, and the total T, we have a quadratic equation for the first n accumulated sum:


We know there are two roots:  and
and 
When  we have real roots. And since the root is positive, we only consider the
we have real roots. And since the root is positive, we only consider the 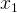 .
.
We compute the value of 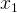 and check if it is a whole integer. This can be done via pythons’ is_integer method. The time/complexity is O(1) considering that the square root is amortized O(1) constant.
and check if it is a whole integer. This can be done via pythons’ is_integer method. The time/complexity is O(1) considering that the square root is amortized O(1) constant.
def f(T):
a = 1
b = 1
c = -2 * T
x = (-b + (b*b-4*a*c)**0.5)/(2*a)
if x.is_integer():
return int(x)
return -1
See the variation of this problem: Teaching Kids Programming – Another Birthday Candles Problem
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
992 wordsLast Post: Adsense/Blog Traffic Declines after ChatGPT is Widely Adopted
Next Post: How to Check Balances of a Bitcoin (BTC) Wallet Address via NodeJs or Python?