Teaching Kids Programming: Videos on Data Structures and Algorithms
KNN Machine Learning Algorithm in Python
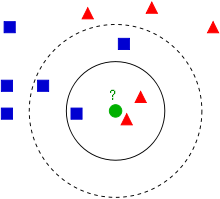
KNN (K Nearnest Neighbours) is a simplest machine learning algorithm. The prediction is made by calculating the K nearest neighbours and then get the average (or median, or weighted average) among then.
K sometimes has to be better odd, so we don’t have even votes. We can increase K value and this might improve prediction accuracy but it takes more time to run the KNN model.
The training dataset has to be fully evaluated. N data points, the time complexity is O(NLogN) as we need to sort to get the K shortest distance. We can improve this to O(KLogN) if we use the heap i.e. O(LogN) to insert a new element or remove an element from heap, and we need to do this K times.
The distance function could be Manhattan distance i.e. 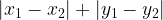 or the Euclidean distance i.e.
or the Euclidean distance i.e. 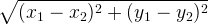
def knn(x, n = 3):
data = {}
for i in range(-1000, 1001):
data[i*0.1] = (i*0.1)**2
cost = [(i, abs(i - x)) for i in data]
cost.sort(key=lambda x:x[1])
return sum(data[x[0]] for x in cost[:n])/n
print(knn(25)) # 625.0066666666668
A more general version of KNN – as the training data set has prepared/known in advance.
data = {}
for i in range(-1000, 1001):
data[i*0.1] = (i*0.1)**2
def knn(x, data, n = 3):
cost = [(i, abs(i - x)) for i in data]
cost.sort(key=lambda x:x[1])
return sum(data[x[0]] for x in cost[:n])/n
print(knn(25, data, 5)) # 625.0200000000001
The prediction algorithm of KNN largely depends on the value of K and the quality of the samples (training dataset). If the samples are bias, then the prediction will be affected as well.
Other KNN Tutorials
- A Short Introduction to K-Nearest Neighbors Algorithm
- The K Nearest Neighbor Algorithm (Prediction) Demonstration by MySQL
- Teaching Kids Programming – Introduction to KNN Machine Learning Algorithm
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
579 wordsLast Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Build Progressive Stairs Row by Row via Simulation, Binary Search or Math Algorithm
Next Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Introduction to Probability and Naive Bayes Theorem