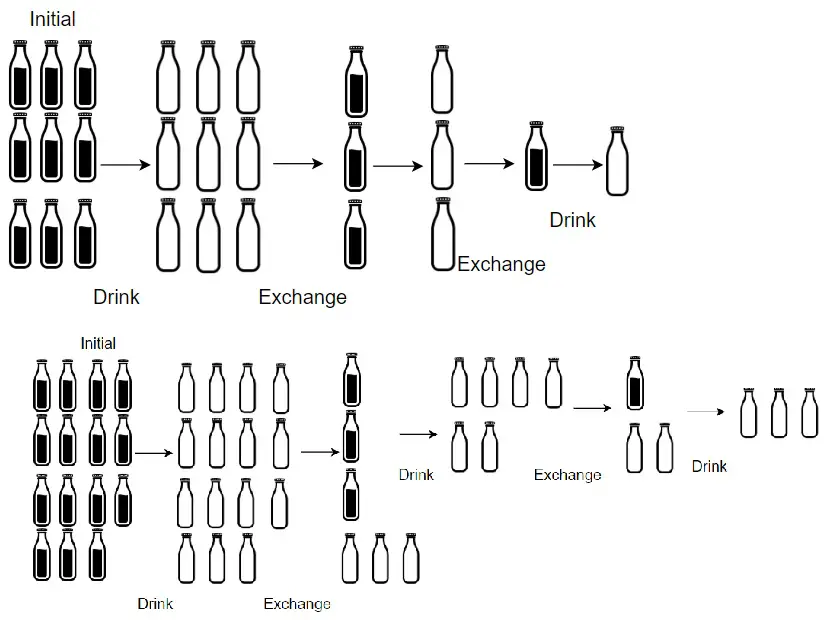
Given numBottles full water bottles, you can exchange numExchange empty water bottles for one full water bottle. The operation of drinking a full water bottle turns it into an empty bottle. Return the maximum number of water bottles you can drink.
Example 1:
Input: numBottles = 9, numExchange = 3
Output: 13
Explanation: You can exchange 3 empty bottles to get 1 full water bottle.
Number of water bottles you can drink: 9 + 3 + 1 = 13.Example 2:
Input: numBottles = 15, numExchange = 4
Output: 19
Explanation: You can exchange 4 empty bottles to get 1 full water bottle.
Number of water bottles you can drink: 15 + 3 + 1 = 19.Example 3:
Input: numBottles = 5, numExchange = 5
Output: 6Example 4:
Input: numBottles = 2, numExchange = 3
Output: 2Constraints:
1 <= numBottles <= 100
2 <= numExchange <= 100
Exchanging Bottles Simulation Algorithm
This is a classic problem to apply the simulation algorithm. If empty bottoes are enough for a exchange, we keep doing this until we can’t exchange for a single bottle. The pitfall is that we have to add the remainder to the next rounds’ emtpy counters.
class Solution:
def numWaterBottles(self, numBottles: int, numExchange: int) -> int:
ans = numBottles
empty = numBottles
while empty >= numExchange:
newBottles = empty // numExchange
ans += newBottles
empty = newBottles + empty % numExchange
return ans
C/C++/Java-style solutions are like:
class Solution {
public int numWaterBottles(int numBottles, int numExchange) {
int ans = numBottles;
int empty = numBottles;
while (empty >= numExchange) {
int newBottles = empty / numExchange;
ans += newBottles;
empty = newBottles + empty % numExchange;
}
return ans;
}
}
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
Last Post: Using CloudFlare Worker Serverless Technology to Deploy a Load Balancer (RPC Node) for Steem Blockchain
Next Post: Remove the Temporary Files (including Windows.old) on Windows 10 to Save Space via Storage Sense