In mathematics, Newton method is an efficient iterative solution which progressively approaches better values. Its definition in [wiki] is
In numerical analysis, Newton’s method (also known as the Newton–Raphson method), named after Isaac Newton and Joseph Raphson, is a method for finding successively better approximations to the roots (or zeroes) of a real-valued function. The algorithm is first in the class of Householder’s methods, succeeded by Halley’s method. The method can also be extended to complex functions and to systems of equations.
[The Newton-Raphson method in one variable is implemented as follows: Given a function ƒ defined over the reals x, and its derivative ƒ ‘, we begin with a first guess 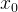 for a root of the function
for a root of the function 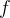 . Provided the function is reasonably well-behaved a better approximation
. Provided the function is reasonably well-behaved a better approximation 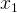 is]
is]
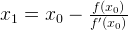
[Geometrically, (x1, 0) is the intersection with the x-axis of a line tangent to f at (x0, f (x0)).
The process is repeated as]
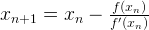
For example, the roots to this function 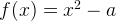 can be obtained using Netwon’s method, which is
can be obtained using Netwon’s method, which is 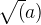 . The derivative function of
. The derivative function of 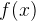 can be computed as
can be computed as
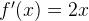
Therefore,
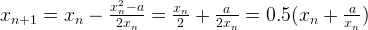
After a few iterations, the method approaches very good approximations of the real-value functions.
#!/usr/bin/env python
# https://helloacm.com
def ntsqrt(n):
sgn = 0
if n < 0:
sgn = -1
n = -n
val = n
while True:
last = val
val = (val + n / val) * 0.5
if abs(val - last) < 1e-9:
break
if sgn < 0:
return complex(0, val)
return val
if __name__ == "__main__":
print ntsqrt(25.0)
Similar to [here] the above computes the sqrt by newton’s method. It also returns the complex number for negative square roots.
The above prints successfully the exact square root 5.0 and the values for each iterations go something like this:
1, 25.0 2, 13.0 3, 7.46153846154 4, 5.40602696273 5, 5.01524760194 6, 5.00002317825 7, 5.00000000005
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
757 wordsLast Post: Binary Search Sqrt
Next Post: Codeforces: A. Almost Prime