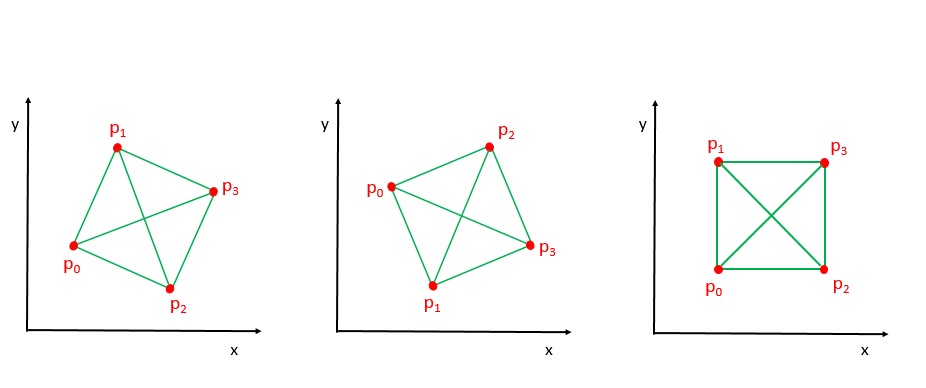
Given the coordinates of four points in 2D space, return whether the four points could construct a square. The coordinate (x,y) of a point is represented by an integer array with two integers.
Example:
Input: p1 = [0,0], p2 = [1,1], p3 = [1,0], p4 = [0,1]
Output: TrueNote:
- All the input integers are in the range [-10000, 10000].
- A valid square has four equal sides with positive length and four equal angles (90-degree angles).
- Input points have no order.
Given four points, we may brute force all four permutation with has O(1) complexity i.e. needs to check 4!=24 cases that if any of those make a square. However, the most elegant and straightforward solution is to compute the distances between each pair, and push the distances to a set. At the end, we just have to check if there are two different lengths and also need to exclude the zeros – which may indicate that at least two points are the same (duplicate).
For example, in the following Java, we create a hash set, and store all possible distances between pairs of points. The complexity is O(1) in terms of space and time.
class Solution {
public boolean validSquare(int[] p1, int[] p2, int[] p3, int[] p4) {
Set<Integer> d = new HashSet();
d.add(dist(p1, p2));
d.add(dist(p1, p3));
d.add(dist(p1, p4));
d.add(dist(p2, p3));
d.add(dist(p2, p4));
d.add(dist(p3, p4));
return d.size() == 2 && (!d.contains(0));
}
private int dist(int[] p1, int[] p2) {
return (int)Math.pow(p1[0] - p2[0], 2) + (int)Math.pow(p1[1] - p2[1], 2);
}
}
The equivalent C++ implementation is below where we use unordered_set to store the unique distance values.
class Solution {
public:
int dist(vector<int> &p1, vector<int> &p2) {
return pow(p1[0] - p2[0], 2) + pow(p1[1] - p2[1], 2);
}
bool validSquare(vector<int>& p1, vector<int>& p2, vector<int>& p3, vector<int>& p4) {
unordered_set<int> d;
d.insert(dist(p1, p2));
d.insert(dist(p1, p3));
d.insert(dist(p1, p4));
d.insert(dist(p2, p3));
d.insert(dist(p2, p4));
d.insert(dist(p3, p4));
return d.size() == 2 && d.count(0) == 0;
}
};
Read also: Teaching Kids Programming – Valid Square Algorithm by Four Points in Cartesian Coordinate System
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
Last Post: Python: Understanding the Importance of EigenValues and EigenVectors!
Next Post: How to Convert Set to Vector in C++?