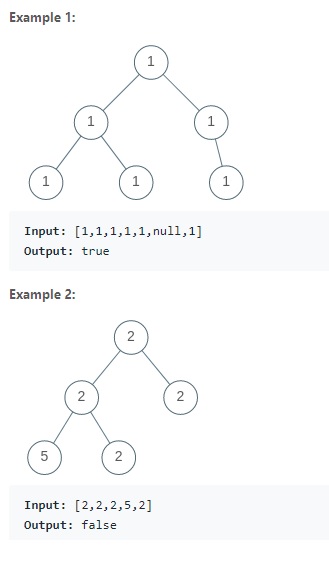
A binary tree is univalued if every node in the tree has the same value. Return true if and only if the given tree is univalued.
A binary tree is uni-valued if all the nodes are of same value. If the root value is different than its left or right node – it is not univalued. Otherwise, we recursively check its left and right sub-trees.
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isUnivalTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return true;
if (root->left != NULL && root->val != root->left->val) return false;
if (root->right != NULL && root->val != root->right->val) return false;
return isUnivalTree(root->left) && isUnivalTree(root->right);
}
};
Alternatively, we just need to verify the left sub tree and the right sub tree contain only the value of the root node.
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isUnivalTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return true;
return dfs(root, root->val);
}
private:
bool dfs(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if (root == NULL) return true;
if (root->val != val) return false;
return dfs(root->left, val) && dfs(root->right, val);
}
};
Both are Depth First Search and have the same time complexity which is O(N) – as each node is at most visited once. The space complexity is also O(N) as the tree could be degenerated into a link list – and the stack depth will be N. The stack is generated and maintained automatically by compiler due to recursion.
Univalue Binary Tree Validation can also be done via BFS: Teaching Kids Programming – Breadth First Search Algorithm to Determine a Univalue Binary Tree
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
419 wordsLast Post: The FizzBuzz Example in Magik Programming Language
Next Post: How to Insert into a Binary Search Tree (Recursive and Iterative)?